Keratoderma (Skin Disorder)
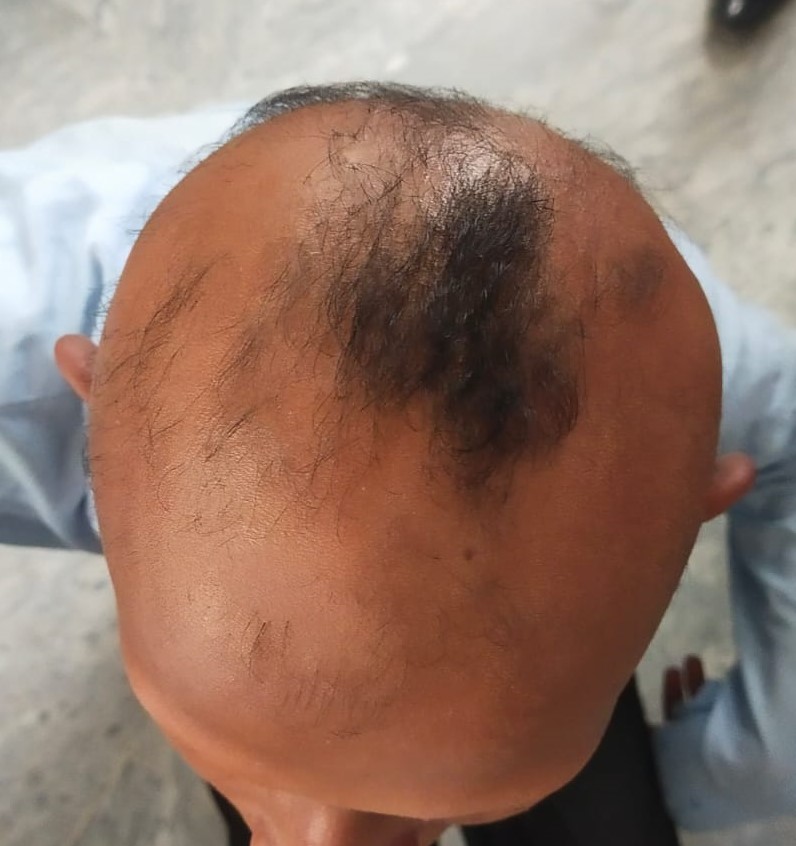
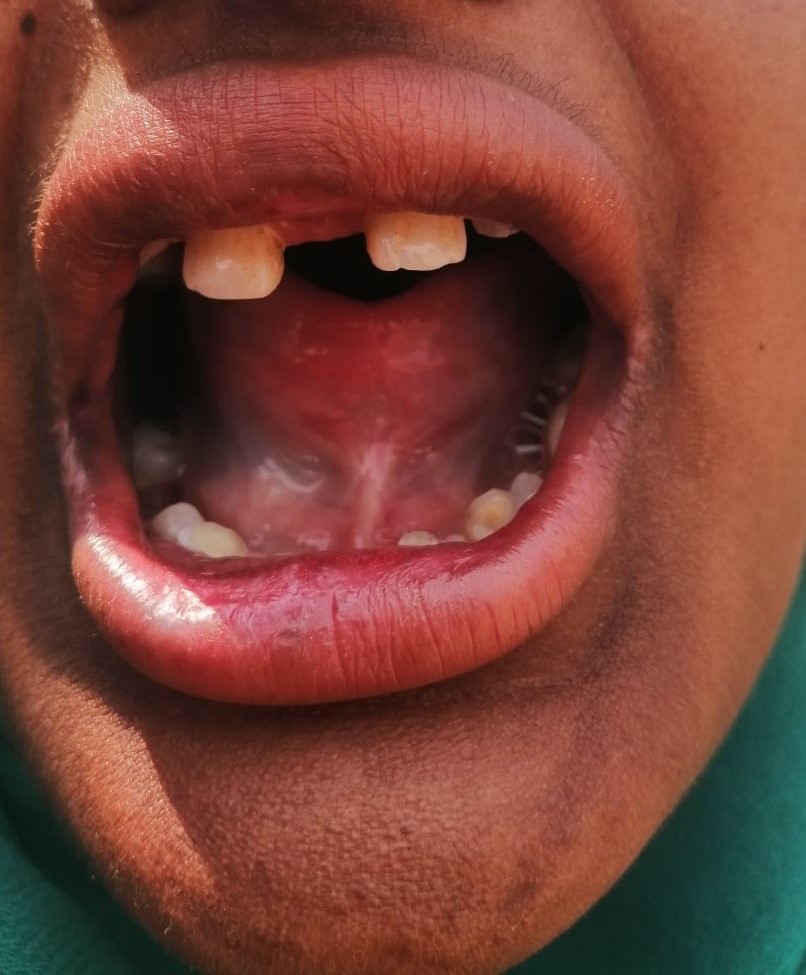
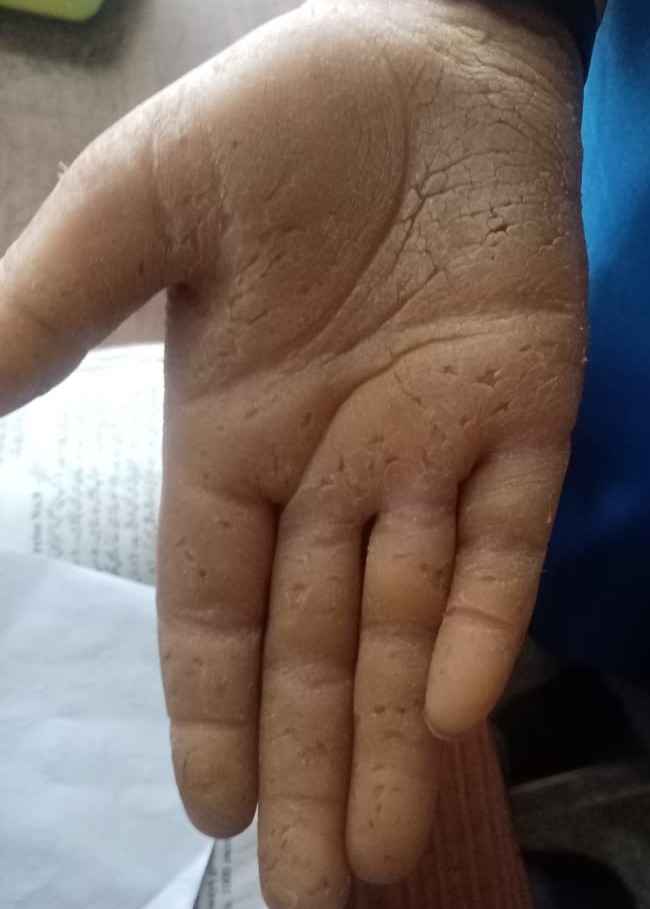
Keratoderma’ is a term used for marked epidermis thickening in skin. Skin become hornlike. It is a heterogeneous group of disorders defined by the presence of focal or generalized thickening of the skin of palm and soles. Inherited keratodermas can be subdivided based on the mode of inheritance, presence of other ectodermal and non-ectodermal findings, and specific genetic and molecular markers. This lab is working on the different types of keratoderma. We aimed to determined the mode of inheritance, molecular basis and mutation in the responsible gene.